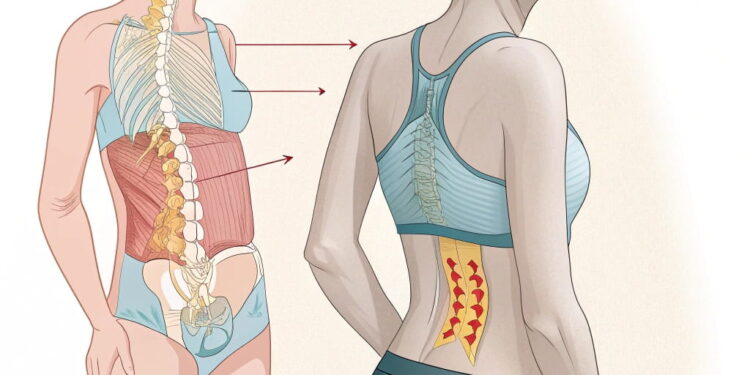
When you think about hernias, you may immediately picture a bulging or protruding mass, typically in the abdomen or groin area. However, many people, especially women, don’t realize that hernias can also contribute to back pain. This often-overlooked connection is crucial for understanding how hernias can affect the body beyond their usual locations. In this article, we’ll explore whether a hernia can cause back pain in females and the symptoms to watch out for.
What is a Hernia?
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot or opening in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. In females, hernias can occur in various areas, including the abdomen, groin (inguinal hernia), or the upper thigh (femoral hernia). The most common type of hernia in women is an inguinal hernia, which happens when part of the intestine bulges through the inguinal canal, a passageway in the lower abdomen.
While hernias are commonly associated with the abdominal area, they can sometimes cause discomfort or pain in areas of the body that are seemingly unrelated, such as the back.
Can a Hernia Cause Back Pain in Females?
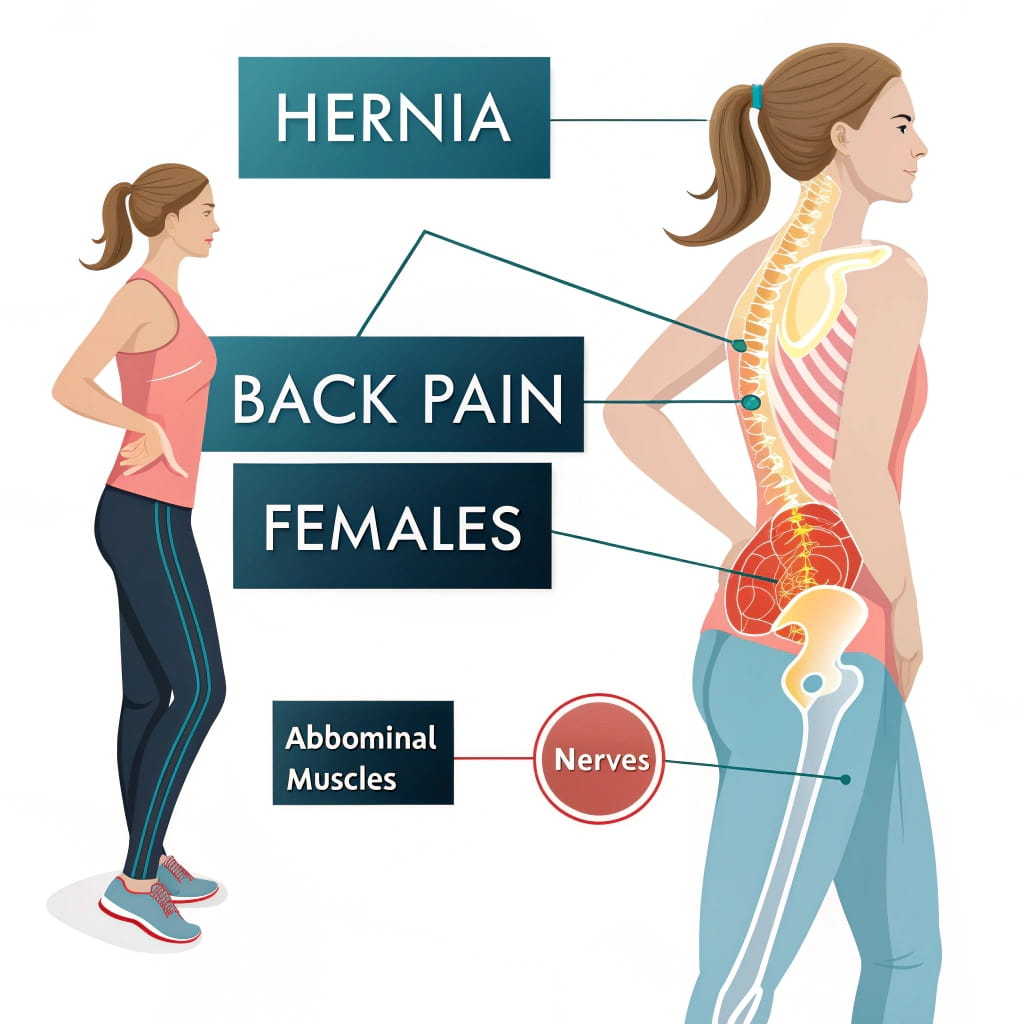
Yes, a hernia can potentially cause back pain in females. This happens in a few ways:
- Nerve Compression
A hernia can put pressure on nearby nerves, including those that travel down the spine or into the lower back. When the hernia pushes against these nerves, it may lead to discomfort or pain that radiates to the back. - Muscle Strain
The pain caused by a hernia can alter your posture and how you move. As you try to compensate for the pain or discomfort caused by the hernia, you might unknowingly strain the muscles in your back, leading to additional back pain. - Visceral Pain Referred to the Back
Hernias that affect the organs, such as abdominal or pelvic hernias, can sometimes lead to referred pain. This means that pain originating in the abdomen or pelvis can be felt in other parts of the body, including the back. Visceral pain is often described as dull and aching but can also feel sharp or cramp-like at times. - Postural Changes
Hernias can also cause postural changes because of the discomfort they cause in the abdominal or groin area. Over time, these changes can stress the back muscles and lead to discomfort or even chronic pain.
Types of Hernias That Can Lead to Back Pain
While any hernia has the potential to lead to back pain, certain types are more likely to cause these issues in women. These include:
- Inguinal Hernia: Though more common in men, women can also develop inguinal hernias. If an inguinal hernia is large or presses on nearby nerves, it could result in lower back pain.
- Femoral Hernia: This type of hernia occurs when tissue pushes through the femoral canal, located in the upper thigh. If the hernia presses on nerves or nearby structures, it may contribute to discomfort that radiates to the back.
- Abdominal Hernia: Hernias that develop in the abdomen or intestines, such as umbilical or incisional hernias, may lead to referred pain in the back. The abdominal wall’s weakening can cause pain that shoots to the lower back.
- Hiatal Hernia: While not directly associated with the back, a hiatal hernia (which occurs when part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm) may cause referred chest or back pain due to digestive issues and acid reflux.
Symptoms of Hernia-Induced Back Pain
If you suspect that a hernia may be causing your back pain, it’s important to look out for specific symptoms:
- Localized pain near the hernia: Pain in the abdominal area or groin that radiates to the lower back.
- Bulging or swelling: You might notice a bulge or lump near the hernia site, especially when standing or coughing.
- Sharp or stabbing pain: Pain that worsens with physical activity, lifting heavy objects, or sudden movements.
- Numbness or tingling: If the hernia is compressing nerves, you may experience a tingling or numb sensation in your back or legs.
If you experience these symptoms, it’s essential to see a healthcare professional for a thorough diagnosis.
Read Also: Back Pain When Coughing – Sharp Back Pain When Coughing Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment!
Diagnosis and Treatment
To determine whether a hernia is causing back pain, your doctor may perform a physical examination and ask about your symptoms. Imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs may also be used to assess the hernia and any related issues in the back.
Treatment will depend on the severity of the hernia and the associated back pain. Common treatments include:
- Conservative management: For smaller hernias, doctors may recommend rest, pain relievers, or physical therapy to manage symptoms and prevethe nt hernia from worsening.
- Surgical intervention: In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the hernia. If the hernia is causing significant pain, surgery may also help relieve back pain by alleviating nerve compression or muscle strain.
- Physical therapy: In some cases, strengthening and stretching exercises can help alleviate both back pain and hernia-related discomfort by improving posture and muscle function.
Prevention and Lifestyle Adjustments
While not all hernias can be prevented, you can reduce the risk of developing one by taking certain precautions:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can put pressure on your abdominal muscles, increasing the risk of a hernia.
- Lift objects properly: Avoid heavy lifting or bending from the waist, which can strain the muscles in the lower abdomen and back.
- Stay active: Regular exercise can help strengthen the muscles of the abdomen and back, reducing the chances of developing a hernia.
- Avoid constipation: Straining during bowel movements can increase pressure on the abdomen and increase the risk of a hernia.
FAQs:
1 Can a hernia cause pain in the lower back?
Yes, a hernia can put pressure on nerves or muscles, leading to lower back pain.
2 What are the common types of hernias that cause back pain in females?
Inguinal hernias, femoral hernias, and abdominal hernias are more likely to cause back pain.
3 How do I know if my hernia is causing back pain?
Symptoms like pain in the abdominal area radiating to the back or a bulging lump can indicate that a hernia is contributing to back pain.
4 Can surgery help relieve both hernia and back pain?
Yes, surgery to repair the hernia can alleviate nerve compression and reduce back pain.
5 What are some ways to prevent a hernia from causing back pain?
Maintaining a healthy weight, lifting objects properly, and strengthening the abdominal and back muscles can help prevent hernia-related back pain.
Conclusion:
While hernias are typically associated with abdominal or groin pain, they can also lead to back pain in females. This can occur due to nerve compression, muscle strain, or referred pain. If you suspect your hernia is causing back pain, it’s essential to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can help alleviate both hernia-related pain and back discomfort, improving your overall quality of life.