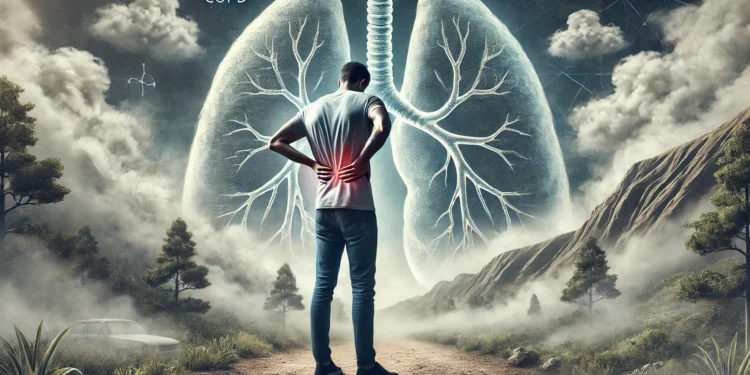
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a serious lung condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It leads to breathing difficulties, persistent cough, and other respiratory issues. However, many people with COPD also experience back pain, which can be frustrating and confusing. In this article, we’ll explore whether COPD can cause back pain, potential reasons for this connection, and how to manage both conditions effectively.
What is COPD?
It makes breathing more difficult by obstructing airflow in the lungs. COPD is typically caused by long-term exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke, air pollution, or occupational hazards.
Common symptoms of COPD include:
- Chronic cough
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Excessive mucus production
- Fatigue
While COPD primarily affects the lungs, it can lead to a range of other symptoms, including back pain.
Can COPD Cause Back Pain?
Yes, COPD can contribute to back pain in several ways. While the disease itself primarily affects the lungs and respiratory system, the physical strain of managing COPD can affect other parts of the body, including the back.
Here are a few ways in which COPD may be linked to back pain:
Muscle Strain from Breathing Difficulties
COPD can make breathing harder, especially during physical exertion. When you struggle to breathe, you may unconsciously overuse muscles in your back and chest, leading to strain and discomfort. Over time, this strain can result in muscle tension, stiffness, and pain in the back.
Postural Changes
People with COPD often develop poor posture due to difficulty breathing. They may hunch forward or adopt a slouched position to help with breathing. This posture can place additional pressure on the spine and muscles in the back, leading to pain or discomfort.
Inactivity and Weak Muscles
COPD patients may avoid physical activity due to shortness of breath or fatigue. Lack of exercise can lead to muscle weakness, particularly in the back, which may contribute to discomfort or pain. Weak muscles are less able to support the spine, leading to strain and back issues.
Osteoporosis and Bone Health
COPD can sometimes lead to osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones, making them more prone to fractures. Long-term use of corticosteroids, which are often prescribed to manage COPD, can increase the risk of osteoporosis. Fragile bones in the spine or ribs can cause back pain, especially when coughing or sneezing.
Increased Inflammation
COPD is a chronic inflammatory disease, and the inflammation in the lungs can sometimes spread to other parts of the body, including the back. Inflammation can affect muscles, joints, and even spinal discs, leading to pain or discomfort in the back.
Symptoms of Back Pain Associated with COPD

If you have COPD and are experiencing back pain, it’s important to recognize the symptoms that may be related to your condition. Some common signs include:
- Dull or aching pain in the lower or upper back.
- Muscle stiffness or tightness, especially after coughing or deep breathing.
- Pain that worsens with activity, such as walking or lifting.
- Pain that improves with rest or a change in posture.
- Numbness or tingling in the back, which may indicate nerve involvement.
How to Manage Back Pain with COPD
Managing both COPD and back pain requires a multifaceted approach. Here are some ways to alleviate discomfort and improve your quality of life:
Breathing Exercises
Breathing exercises can help improve lung function and reduce the strain on your back muscles. Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing and pursed-lip breathing can help you breathe more efficiently and reduce the need to overuse back muscles.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
A physical therapist can guide you through exercises that strengthen your back muscles, improve posture, and enhance lung function. Regular physical activity is essential for preventing muscle weakness and improving overall mobility.
Posture Correction
Focusing on good posture can alleviate pressure on the spine and back muscles. If you have COPD, work on maintaining an upright posture, especially when breathing. Proper ergonomics while sitting and standing can also help reduce back pain.
Pain Relief Medication
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage mild back pain. For more severe discomfort, your doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants or other stronger pain medications.
Osteoporosis Management
If you’re at risk for osteoporosis, your doctor may recommend calcium and vitamin D supplements or medications to strengthen your bones. This can help reduce the risk of fractures that could cause back pain.
Corticosteroid Alternatives
If you’re experiencing side effects from corticosteroid use, such as osteoporosis, talk to your doctor about alternative medications or treatment options for managing your COPD.
When to See a Doctor
If you’re experiencing significant or persistent back pain with COPD, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider. Back pain can sometimes be a sign of a more serious condition, such as a spinal injury, infection, or herniated disc. Your doctor will be able to assess your symptoms, conduct necessary tests, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
FAQs:
1 Can COPD cause back pain?
Yes, COPD can lead to back pain due to muscle strain, posture changes, inactivity, and complications like osteoporosis.
2 How does COPD affect posture and back pain?
COPD can cause poor posture, leading to extra pressure on the spine and back muscles, which may result in pain.
3 What exercises help with back pain and COPD?
Breathing exercises, physical therapy, and posture correction can help reduce back pain and improve lung function.
4 Can osteoporosis from COPD cause back pain?
Yes, long-term corticosteroid use in COPD patients can lead to osteoporosis, making the bones fragile and increasing the risk of back pain.
5 When should I see a doctor for back pain with COPD?
See a doctor if back pain persists, worsens, or if it’s associated with severe symptoms like numbness or difficulty moving.
Conclusion:
Back pain in people with COPD is not uncommon, and it can be caused by a combination of muscle strain, poor posture, inactivity, or complications like osteoporosis. Managing both COPD and back pain requires a comprehensive approach, including breathing exercises, physical therapy, good posture, and pain management. By taking the right steps, you can reduce discomfort and improve your overall well-being while managing your COPD symptoms. If you’re experiencing back pain, speak to your healthcare provider to find the most effective treatment plan for your needs.
Read More Relevant Article:
- Read Also: Compression Shirt for Back Pain: The Ultimate Guide to Relief and Comfort – Back Pain Compression Shirt!
- Read Also: Back Pain MDM: Understanding Medical Decision Making for Back Pain Treatment – Medical Decision Making for Back Pain!
- Read Also: Can Heat Make Back Pain Worse? Understanding the Impact of Heat on Back Pain – Can Heat Exacerbate Back Pain!