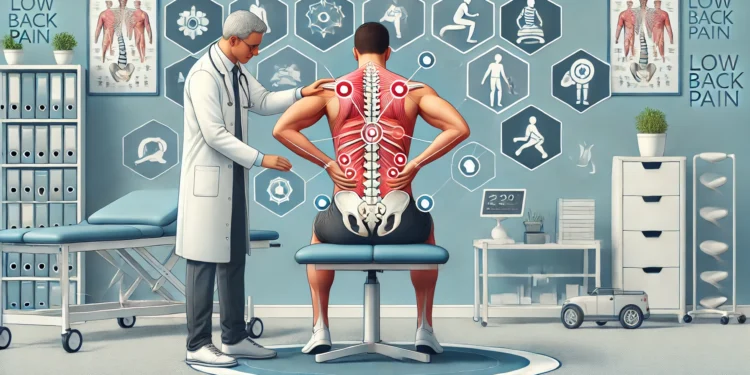
Low back pain (LBP) is one of the most common reasons people seek medical attention, affecting millions worldwide. It can range from a mild discomfort to debilitating pain, which can significantly impact daily life. A key approach to managing LBP is understanding the treatment-based classification system. This method categorizes patients based on specific symptoms and characteristics, helping healthcare providers develop the most effective treatment plan. In this article, we’ll explore what treatment-based classification (TBC) for low back pain is, how it works, and the different types of classifications that can guide treatment.
What is Treatment-Based Classification for Low Back Pain?
Treatment-based classification (TBC) is a system used by healthcare professionals to categorize individuals with low back pain into specific groups. By evaluating various factors such as pain intensity, movement patterns, and physical function, clinicians can tailor a treatment approach to suit the patient’s specific needs.
The idea behind TBC is to identify the underlying causes and characteristics of the pain and then match the treatment to the type of pain. This targeted approach helps to improve outcomes, reduce recovery time, and prevent chronic pain.
Read Also: Back Pain When Coughing – Sharp Back Pain When Coughing Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment!
How Treatment-Based Classification Works
Treatment-based classification for low back pain generally involves assessing a variety of factors, including:
- Pain location and intensity: Is the pain confined to the lower back, or does it radiate to the legs? Is it sharp or dull?
- Movement patterns and physical function: How well can the patient perform daily activities? Are there any movement restrictions?
- Response to previous treatments: Has the patient responded well to past interventions, or have they had difficulty finding relief?
- Medical history: Any pre-existing conditions such as osteoarthritis, herniated discs, or spinal stenosis can influence classification and treatment plans.
Based on these assessments, clinicians assign a treatment plan aimed at alleviating pain, improving function, and addressing the underlying cause.
Types of Treatment-Based Classifications for Low Back Pain

There are different treatment-based classification systems, but most focus on categorizing low back pain into a few broad types based on the patient’s condition. Below are some common TBC categories:
1. Mechanical Pain (Subacute and Chronic)
Mechanical low back pain occurs when the pain is primarily due to the movement and mechanics of the spine. This may include conditions such as muscle strain, ligament sprain, or disc degeneration. The pain usually worsens with certain activities, such as bending or lifting, and improves with rest or specific movements.
Treatment Options:
- Physical therapy focusing on strengthening and improving flexibility in the back and core muscles.
- Manual therapy, including spinal manipulation, to alleviate pain and improve movement.
- Postural training to help with correct body mechanics during daily activities.
2. Radicular Pain (Sciatica or Nerve Pain)
Radicular pain refers to pain that radiates down from the back to the legs, commonly due to a pinched nerve or herniated disc. This type of pain is often sharp, shooting, and can lead to numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected leg.
Treatment Options:
- Medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or oral corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
- Epidural steroid injections to relieve nerve irritation and swelling.
- Nerve mobilization techniques or physical therapy to improve nerve function and relieve pressure on the affected nerve.
3. Specific Exercise-Based Classification
For individuals with low back pain, specific exercise-based classifications involve targeting specific exercise programs to improve strength, flexibility, and stability based on the assessment. These may include exercises focused on the core, hip flexors, hamstrings, or spinal alignment.
Treatment Options:
- Core strengthening exercises to support the spine and reduce strain on the lower back.
- Stretching routines to improve flexibility in the hips, hamstrings, and lower back muscles.
- Stability exercises to promote better posture and movement patterns.
4. Non-Specific Low Back Pain
Non-specific low back pain is one of the most common classifications. It refers to pain that cannot be linked to a specific underlying condition such as a herniated disc or spinal stenosis. This pain is typically more diffuse and can result from factors like poor posture, overuse, or stress.
Treatment Options:
- Physical therapy focusing on strengthening and mobility exercises.
- Lifestyle changes, such as improving posture, weight management, and ergonomic work environments.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to address any psychological factors that may contribute to pain, such as stress or anxiety.
The Benefits of Treatment-Based Classification for Low Back Pain
Personalized Treatment Plans:
By classifying low back pain into categories based on individual needs, TBC ensures that each patient receives the most effective treatment tailored to their specific condition.
Faster Recovery:
Identifying the root cause of low back pain allows for more focused interventions, which can lead to faster recovery times and improved outcomes.
Prevention of Chronic Pain:
Proper treatment can help prevent acute pain from turning into chronic back pain, reducing long-term disability and improving quality of life.
Better Patient Understanding:
The classification process helps patients understand their condition, which can improve compliance with treatment plans and lead to better self-management of their back pain.
When to Seek Professional Help
While treatment-based classification can be helpful, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation of your low back pain. A healthcare professional can assess your symptoms, perform diagnostic tests, and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan. If your pain persists for more than a few weeks, or if it’s accompanied by symptoms like numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs, it’s crucial to seek medical attention to rule out more serious conditions.
FAQs:
1. What is treatment-based classification for low back pain?
TBC is a method used to categorize low back pain based on symptoms, such as pain location and intensity, to develop personalized treatment plans.
2. What are the different types of treatment-based classifications for low back pain?
Common types include mechanical pain, radicular pain (nerve pain), exercise-based classifications, and non-specific low back pain.
3. How does treatment-based classification help manage low back pain?
By assessing symptoms and conditions, TBC enables healthcare providers to create targeted treatments that can lead to faster recovery and improved outcomes.
4. Can treatment-based classification prevent chronic back pain?
Yes, it helps by providing focused treatment to prevent acute pain from becoming chronic, improving long-term pain management.
5. When should I seek professional help for low back pain?
Seek professional help if your pain lasts more than a few weeks or is accompanied by symptoms like numbness, tingling, or leg weakness.
Conclusion:
Treatment-based classification for low back pain is a valuable method for diagnosing and managing pain. By grouping individuals based on their symptoms and condition, clinicians can create targeted treatment plans that improve outcomes and reduce recovery times. Whether the pain is mechanical, radicular, or non-specific, TBC offers a structured way to address the pain effectively.If you’re dealing with low back pain, consider seeking a healthcare provider who uses treatment-based classification to help guide your recovery. With the right approach, you can manage your back pain and get back to living an active, healthy life.