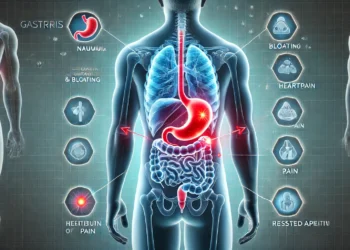
Experiencing back pain after eating can be frustrating and uncomfortable. You might be wondering why your back hurts after a meal and what you can do to alleviate it. In this article, we’ll explore common causes of back pain after eating, symptoms to watch for, and treatment options to help you manage the discomfort.
Why Does My Back Hurt After Eating?
Back pain after eating is often linked to digestive issues, poor posture, or other underlying health conditions. The act of eating involves more than just digestion; your posture, stomach, and internal organs can all contribute to the discomfort. Understanding the potential causes of back pain after eating is key to finding the right treatment.
Read Also: Middle Back Pain Around the Rib Cage – Pain in the Middle Back Near the Rib Cage!
Common Causes of Back Pain After Eating
Digestive Issues
Acid Reflux or GERD: When stomach acid moves up into the esophagus, it can cause pain in the chest and back. This often happens after a heavy meal and can be worsened by lying down or reclining.
Indigestion: Overeating, eating too quickly, or consuming spicy or fatty foods can cause indigestion. This can lead to discomfort or pain in the stomach area, which can radiate to the back.
Gas and Bloating: Excessive gas buildup in the stomach or intestines can cause bloating and discomfort, which may extend to the lower or upper back.
Poor Posture
After eating, many people tend to slump or lie down, which can lead to muscle strain in the back. Poor posture while sitting or standing can also lead to discomfort, especially if you’re not supporting your spine properly.
Pancreatitis
Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis) can cause pain in the upper back, especially after eating. The pain is often sharp and may worsen after consuming fatty foods.
Gallbladder Issues
Gallstones or gallbladder inflammation can result in pain after eating, particularly after consuming fatty foods. This pain often radiates to the back, especially the right side.
Kidney Stones or Infection
Kidney stones or a kidney infection can cause intense pain in the back, which may worsen after eating. The pain typically occurs in the lower back or sides and may be accompanied by other symptoms like pain while urinating or fever.
Herniated Disc or Back Injury
A herniated disc or other spinal issues can cause back pain that worsens after eating, particularly if you’re sitting for long periods or have poor posture during and after meals.
Symptoms to Watch For
The type of pain and accompanying symptoms can help determine the cause of your back pain after eating:
- Sharp or stabbing pain: This can indicate issues like pancreatitis, gallbladder problems, or a herniated disc.
- Dull or aching pain: This is more commonly related to digestive problems like acid reflux, indigestion, or gas buildup.
- Pain that worsens after fatty meals: This suggests potential gallbladder or pancreas-related issues.
- Pain that radiates from the chest to the back: This can be a sign of acid reflux or GERD.
- Lower back pain: This can be linked to digestive issues, kidney problems, or muscle strain from poor posture.
When to Seek Medical Help
While mild discomfort after eating may not be cause for concern, it’s important to seek medical attention if:
- The pain is severe or persistent.
- You experience additional symptoms like fever, nausea, vomiting, or changes in bowel movements.
- The pain is accompanied by chest pain or difficulty breathing.
- You have a history of digestive issues, gallstones, or kidney problems.
Treatment Options for Back Pain After Eating
Dietary Adjustments
Avoiding heavy, greasy, or spicy foods can help reduce the risk of indigestion, acid reflux, and bloating. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can also help prevent discomfort.
Stay hydrated and include fiber-rich foods in your diet to promote healthy digestion and prevent constipation.
Improve Posture
Sit up straight while eating and avoid slouching. If you tend to recline or lie down after eating, try to stay upright for at least 30 minutes to help your body digest the food more effectively.
Consider using a back support cushion or chair with proper lumbar support to maintain good posture during and after meals.
Medications
Over-the-counter antacids or acid reducers can help alleviate symptoms of acid reflux or GERD.
Pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen may help with mild discomfort caused by muscle strain or digestive issues.
Manage Stress
Stress can contribute to digestive issues and back pain. Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, yoga, or meditation, can help reduce tension in your body and alleviate discomfort after meals.
Physical Therapy
If the pain is related to muscle strain or a herniated disc, physical therapy can help improve posture, strengthen muscles, and reduce pain. A physical therapist can guide you through exercises to support your spine and improve your back health.
Seek Medical Treatment for Underlying Conditions
If your back pain after eating is related to a more serious condition, such as pancreatitis, gallstones, or kidney stones, your doctor may recommend further treatment, such as medications, lifestyle changes, or surgery.
Prevention Tips for Back Pain After Eating
While not all cases of back pain after eating are preventable, here are a few tips to help reduce your risk:
- Eat slowly and avoid overeating: Eating too quickly can lead to indigestion, bloating, and back pain. Take your time to chew your food properly.
- Practice good posture: Sit with your back straight and avoid slouching, especially after meals.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight, improve digestion, and strengthen your back muscles.
- Manage stress: Reducing stress can help prevent digestive problems and muscle tension.
FAQs:
1 Why does my back hurt after I eat?
Back pain after eating can be caused by digestive issues, poor posture, or underlying conditions like gallstones, pancreatitis, or kidney stones.
2 Can poor posture cause back pain after eating?
Yes, slouching or reclining after meals can strain your back muscles and lead to discomfort.
3 How can I relieve back pain after eating?
Dietary changes, improving posture, and using over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate the pain. For more serious conditions, consult your doctor.
4 When should I see a doctor for back pain after eating?
Seek medical attention if the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms like fever, nausea, or chest pain.
5 Can stress cause back pain after eating?
Yes, stress can contribute to digestive problems and muscle tension, both of which can lead to back pain after meals.
Conclusion:
Back pain after eating can be caused by a variety of factors, from digestive issues and poor posture to more serious conditions like gallstones or pancreatitis. Identifying the underlying cause is essential for finding the right treatment and managing your symptoms. By making dietary adjustments, improving posture, and seeking appropriate medical treatment, you can reduce your risk of experiencing back pain after eating and improve your overall well-being.
Read More Relevant Article:
- Read Also: Upper Back Hurts When I Breathe – Pain in the Upper Back with Deep Breaths!
- Read Also: Lower Back Pain in the Morning That Goes Away – Morning Lower Back Pain That Disappears After a While!
- Read Also: Gastritis Symptoms and Back Pain – Signs of Gastritis and Their Connection to Back Pain!