Experiencing upper back pain when breathing can be concerning, especially if the pain is persistent or intense. If you’ve ever wondered why your upper back hurts when you breathe, you’re not alone. This condition can stem from various causes, ranging from muscle strain to more serious health conditions. In this article, we’ll explore the potential causes, symptoms, and treatment options for upper back pain associated with breathing.
Common Causes of Upper Back Pain When Breathing
Understanding the underlying causes of upper back pain when breathing can help you determine the appropriate course of action for relief. Below are some common causes:
Read Also: Vertebrogenic Low Back Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment – Spinal-Origin Low Back Pain!
1. Muscle Strain
One of the most common causes of upper back pain, especially when breathing, is muscle strain. Overexertion from activities like lifting, poor posture, or sudden movements can cause the muscles in your upper back to become overstretched or torn. This can result in discomfort that worsens when you inhale deeply or cough.
2. Costovertebral Joint Dysfunction
The costovertebral joints are where the ribs meet the spine in the upper back. Dysfunction in these joints, caused by injury, inflammation, or arthritis, can cause pain that intensifies with breathing. When you breathe in, the ribs expand, which can aggravate the affected joints, leading to pain.
3. Rib Injury or Fracture
A rib injury, whether from trauma, a fall, or an accident, can cause upper back pain when you breathe. When the ribs move during respiration, a fractured or bruised rib can cause sharp pain in the upper back area, particularly during deep breathing or coughing.
4. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) occurs when nerves or blood vessels in the upper chest are compressed. This can lead to pain, numbness, and tingling in the upper back, neck, and shoulders, and can worsen with deep breathing or physical activity. TOS is commonly associated with poor posture or repetitive overhead motions.
5. Pleurisy
Pleurisy is an inflammation of the lining around the lungs (the pleura), often caused by infections like pneumonia or viral illnesses. The pain from pleurisy typically intensifies when you take a deep breath, cough, or sneeze, and it can be felt in the upper back or chest.
6. Herniated Disc
Although herniated discs are more common in the lower back, they can also occur in the upper spine (thoracic spine). A herniated disc can put pressure on the nerves in your upper back, causing pain that worsens with breathing or certain movements.
7. Heart-Related Issues
In rare cases, upper back pain when breathing can be a symptom of a heart condition. Conditions like angina or even a heart attack can cause discomfort that radiates to the upper back. If the pain is severe, sudden, or accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness, it’s essential to seek immediate medical attention.
Symptoms to Watch For
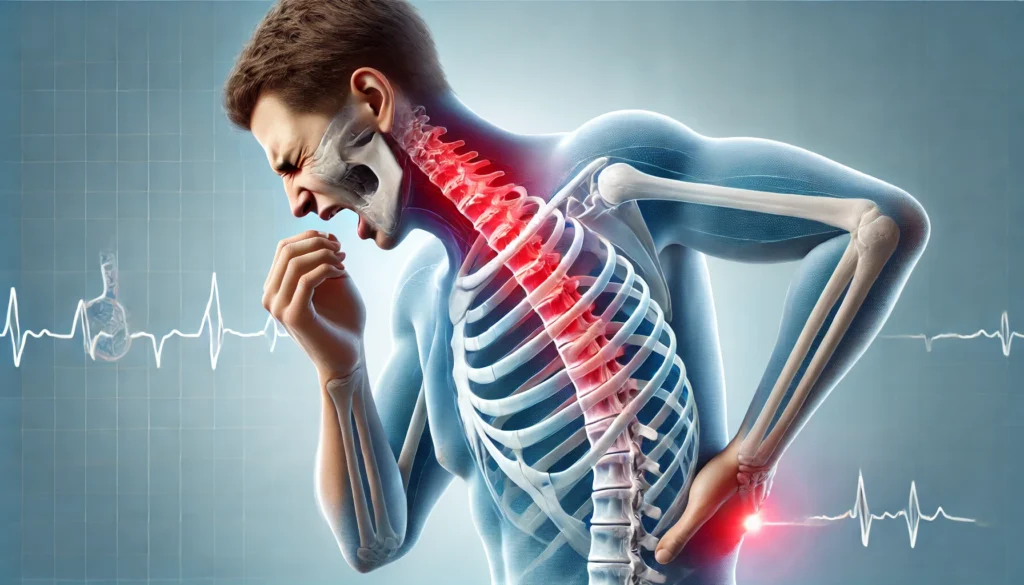
If you’re experiencing upper back pain when breathing, it’s important to monitor the symptoms to determine if medical attention is necessary. Key symptoms include:
- Sharp or stabbing pain: Pain that intensifies with deep breathing or coughing.
- Muscle stiffness: The feeling of tightness or discomfort in the upper back muscles.
- Radiating pain: Pain that moves from the upper back to the chest, neck, or shoulders.
- Difficulty breathing: Shortness of breath or feeling like you can’t take a full breath.
- Swelling or bruising: Visible signs of injury, especially after trauma or a fall.
When to See a Doctor
If your upper back pain is persistent, severe, or accompanied by other symptoms like shortness of breath, dizziness, or chest pain, it’s important to seek medical attention. A healthcare provider can perform a thorough evaluation, including imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans, to determine the exact cause of your pain.
Treatment Options for Upper Back Pain When Breathing
Treatment for upper back pain associated with breathing depends on the underlying cause. Some common treatment options include:
Rest and Ice/Heat Therapy
If muscle strain is the cause, rest and alternating ice and heat therapy can help reduce inflammation and ease muscle tightness. Applying ice to the area for 15-20 minutes can help reduce swelling, while heat can promote blood flow and relax the muscles.
Physical Therapy
For conditions like costovertebral joint dysfunction or muscle strain, physical therapy may be recommended. A physical therapist can guide you through exercises to strengthen the muscles in your upper back and improve posture, which can alleviate pain.
Pain Medications
Over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage mild to moderate pain. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications or muscle relaxants if the pain is more severe.
Injections
For more severe cases, particularly with rib injuries or thoracic outlet syndrome, your doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Surgical Intervention
In cases where the pain is caused by a herniated disc or other structural problems in the spine, surgery may be necessary. Surgical options can include discectomy or other procedures to relieve pressure on the nerves.
Prevention Tips for Upper Back Pain
Preventing upper back pain can be achieved by adopting healthy habits and making certain lifestyle changes:
- Maintain good posture: Poor posture is a major cause of upper back pain. Practice sitting and standing with your back straight and shoulders back.
- Exercise regularly: Strengthen your back and core muscles with exercises to provide better support for your spine.
- Avoid heavy lifting: If you must lift heavy objects, use proper technique to avoid straining your back.
- Take breaks: If you’re sitting for long periods, make sure to get up, stretch, and move around to avoid stiffness in your back.
FAQs:
1 What causes upper back pain when breathing?
It can be caused by muscle strain, rib injuries, costovertebral joint dysfunction, pleurisy, or thoracic outlet syndrome.
2 When should I see a doctor for upper back pain?
If the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by shortness of breath, chest pain, or dizziness, it’s important to seek medical attention.
3 Can poor posture cause upper back pain when breathing?
Yes, poor posture can strain the muscles in the upper back, leading to discomfort, especially when breathing deeply.
4 How is upper back pain diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical exam and may include imaging tests like X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans to identify the cause.
5 What treatments are available for upper back pain when breathing?
Treatment may include rest, ice/heat therapy, physical therapy, pain medications, and in severe cases, injections or surgery.
Conclusion:
Upper back pain when breathing can have a variety of causes, ranging from muscle strain to serious health conditions like heart issues or pleurisy. If you’re experiencing persistent or severe pain, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to pinpoint the cause and determine the appropriate treatment. By understanding the potential causes and taking steps to improve your posture and overall health, you can manage and prevent upper back pain more effectively.
Read More Relevant Article:
- Read Also: How to Get 100% VA Disability for Back Pain – Steps to Secure 100% VA Disability Benefits for Chronic Back Pain!
- Read Also: Upper Back Pain in Pneumonia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment – Experiencing Upper Back Pain with Pneumonia!
- Read Also: Back And Pain Center at Burlington Building – Back & Pain Relief Center at the Burlington Building!